Npk: The Key To Healthy Thriving Plants
Title: NPK: The Key to Healthy Thriving Plants
Introduction:
Plants need a variety of nutrients to grow healthy and strong. The three most important nutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are collectively known as NPK.
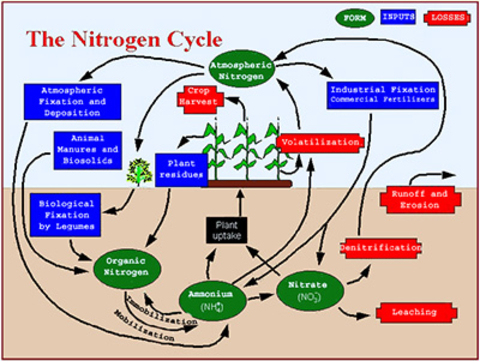
Nitrogen is essential for plant growth. It is involved in the production of chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color. Chlorophyll is also involved in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
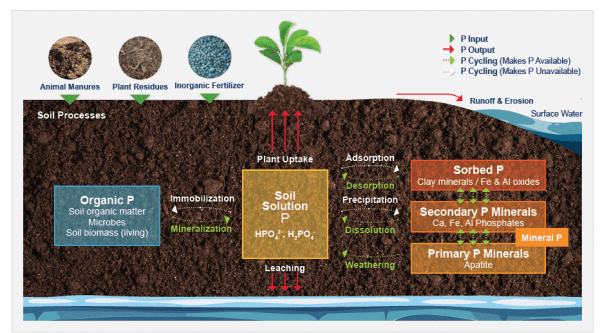
Phosphorus is involved in a number of important plant functions, including energy transfer, cell division, and flowering. It is also essential for the development of strong roots.
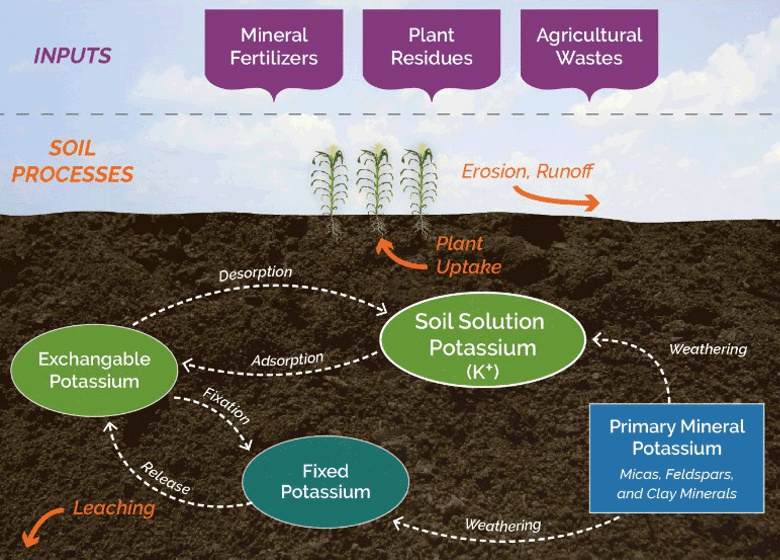
Potassium is involved in a number of important plant functions, including water transport, disease resistance, and cold tolerance. It is also essential for the production of carbohydrates.
Main Content:
The amount of NPK that plants need varies depending on the type of plant and the stage of growth. For example, leafy vegetables need more nitrogen than fruit-bearing plants.
There are a number of ways to provide plants with NPK. One way is to use a commercial fertilizer. Commercial fertilizers are available in a variety of formulas, so you can choose one that is specifically designed for your type of plant.
Another way to provide plants with NPK is to use organic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are made from natural materials, such as manure, compost, and bone meal. They are a good choice for gardeners who want to avoid using synthetic fertilizers.
No matter which method you choose, it is important to follow the directions on the fertilizer label. Over-fertilizing can be just as harmful as under-fertilizing.
Conclusion:
NPK is essential for healthy plant growth. By providing your plants with the right balance of these nutrients, you can help them grow strong and healthy.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are the three main nutrients that plants need to grow healthy and strong. Nitrogen is responsible for leaf growth, phosphorus is needed for root development, and potassium helps with overall plant health.
The amount of NPK that a plant needs varies depending on the type of plant, the soil conditions, and the climate. If a plant is not getting enough of one of these nutrients, it will show signs of deficiency. For example, a nitrogen deficiency will cause the leaves to turn yellow, while a phosphorus deficiency will stunt the plant's growth.
To ensure that your plants are getting the nutrients they need, you can have your soil tested. This will tell you the levels of NPK in your soil and help you determine how much fertilizer you need to apply.
You can also learn more about NPK and how to fertilize your plants by visiting Garden Wiki. This website has a wealth of information on plant nutrition, including articles, videos, and calculators.
FAQ of nitrogen phosphorus and potassium
- What are NPK fertilizers?
NPK fertilizers are chemical fertilizers that contain the three primary macronutrients needed for plant growth: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are essential for plant development, and they are often deficient in soil. NPK fertilizers can help to improve plant growth and health.
- What are the benefits of using NPK fertilizers?
There are many benefits to using NPK fertilizers, including:
* Increased plant growth and yield
* Improved plant health and vigor
* Increased resistance to pests and diseases
* Improved soil quality
- How do I know which NPK fertilizer is right for my plants?
The type of NPK fertilizer that you need will depend on the type of plants you are growing and the specific nutrient deficiencies in your soil. You can get a soil test to determine the nutrient levels in your soil, and then you can choose a fertilizer that will help to correct the deficiencies.
- How do I apply NPK fertilizers?
NPK fertilizers can be applied to soil or foliage. Soil application is the most common method, and it is usually done by broadcasting the fertilizer over the soil surface. Foliar application is less common, but it can be effective for plants that are deficient in a specific nutrient.
- What are the risks of using NPK fertilizers?
NPK fertilizers can be harmful to the environment if they are not used properly. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff, which can pollute waterways. It is important to follow the directions on the fertilizer label to avoid these risks.
- Are there any natural alternatives to NPK fertilizers?
Yes, there are a number of natural alternatives to NPK fertilizers. These include compost, manure, and bone meal. These natural fertilizers can provide the same nutrients as NPK fertilizers, but they are less likely to pollute the environment.





Post a Comment for "Npk: The Key To Healthy Thriving Plants"